Valery Fedorov1,2, Alim Zalihanov1,3
1Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
2E-mail:fedorov.msu@mail.ru, 3E-mail: bulungu@yandex.ru
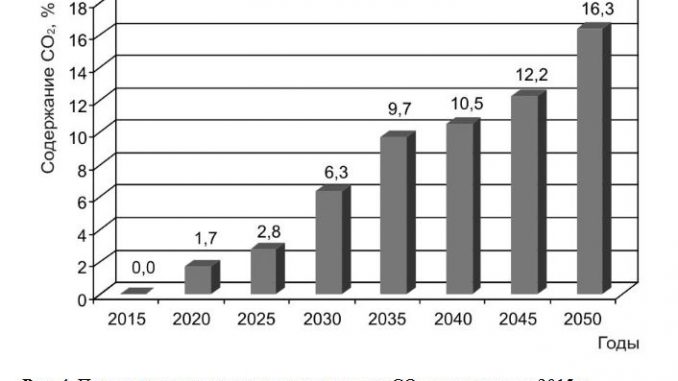
Abstract. The article presents an evaluative forecast for the change of the Earth’s temperature behavior parameters in XXI century that was worked out with a regression model and insolation contrast range as a predictor. The study discovered that in 2100 the anomalies of surface air temperatures (relatively to 1961-1990 average) are expected to be 1.63, 2.06 and 1.20°C for the Earth average, Northern and Southern Hemispheres respectively. The temperature anomalies for the Ocean surface waters will rise until 2100 up to 1.07°С, 1.12, and 1.04°С for the World Ocean average, Northern and Southern Hemispheres respectively. The work also forecasts the content of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. According to the authors’ scenario it will increase up to 2050 comparatively to 2015 (when the Paris Climate Agreement was adopted) by 65.5 ppm. So, the expected growth is some 16.3% independently on efforts of the Paris Agreement participants.
Keywords: estimative forecast, regression model, insolation contrast range, global temperature, carbon dioxide content.
